diff options
Diffstat (limited to 'writeups/test-ipv6.com/broken_mtu1280.test-ipv6.com.md')
| -rw-r--r-- | writeups/test-ipv6.com/broken_mtu1280.test-ipv6.com.md | 87 |
1 files changed, 87 insertions, 0 deletions
diff --git a/writeups/test-ipv6.com/broken_mtu1280.test-ipv6.com.md b/writeups/test-ipv6.com/broken_mtu1280.test-ipv6.com.md new file mode 100644 index 0000000..fe4bd17 --- /dev/null +++ b/writeups/test-ipv6.com/broken_mtu1280.test-ipv6.com.md @@ -0,0 +1,87 @@ +# False PMTUD result due to mtu1280.test-ipv6.com not set up correctly +I came across a strange problem where **test-ipv6.com** test fails while IPv6 +connectivity works just fine. Turns out, there was nothing wrong with the +connectivity provided by Comviq, low-cost MVNO of Tele2. In summary, the false +result on the particular network is due to the following factors. + +- mtu1280.test-ipv6.com is not set up correctly. The ACK packet for the large + packets still make it to the client +- Out of order delivery of IP packets over Tele2's mobile network +- The strict validation of ICMPv6 packets in Linux kernel + +## mtu1280.test-ipv6.com ACK's large packets +It seems that the packet too large message is "soft-simulated" on the host +rather than on a node that sits between the test host and the internet because +the ICMP packet is originated from the same source address and the large packet +that is not supposed to be undeliverable to the host is apparently delivered and +ACK'd. + +The ICMP packet having the same source and destination address as the host does +not make sense because the MSS of both endpoints are exchanged in the sync phase +using the options header. So it's usually the routers in old/exotic/tunneled L2 +segments that send such packets. + +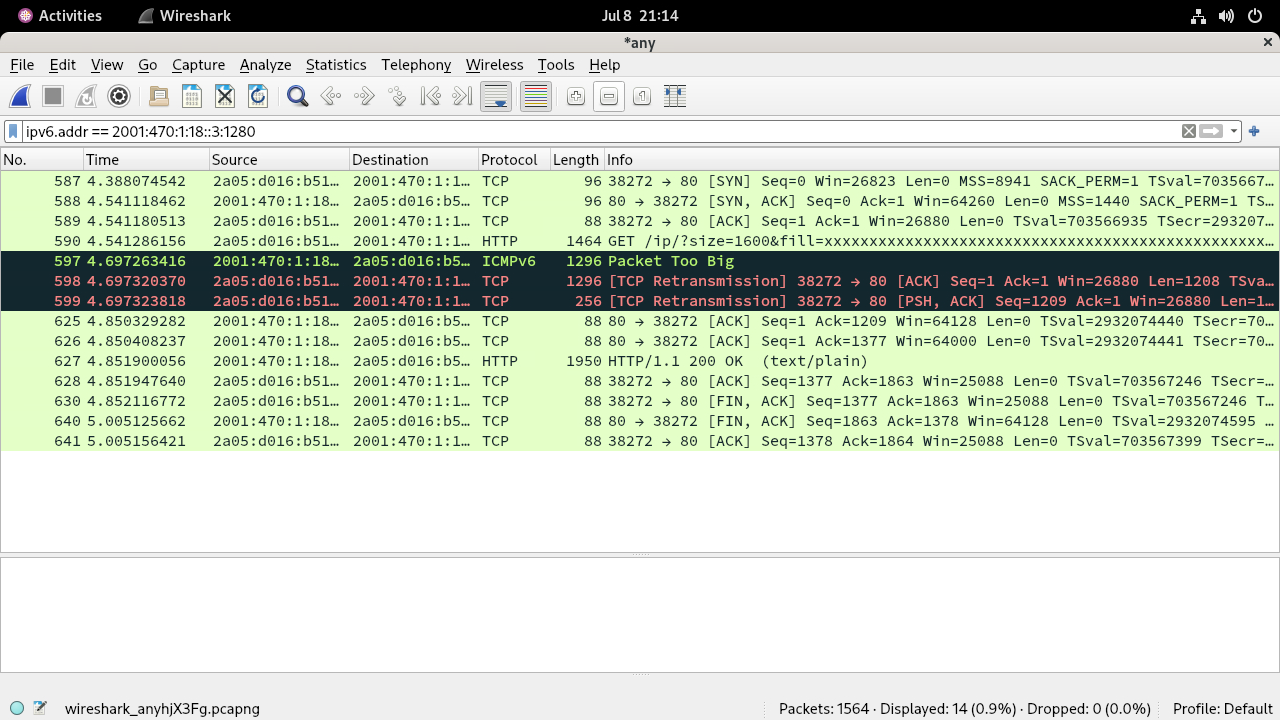 + +Under the "normal" conditions, the ICMP packet reaches the client end before the +ACK packet so the kernel is able to validate the ICMP message and cache the +PMTU. The retransmission is performed and the ACK is effectively ignored and +counted as duplicate ACK(on BSD systems). + +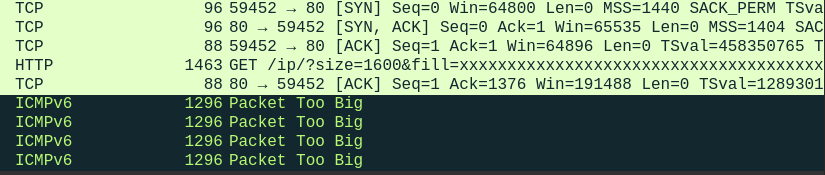 + +In case of the ACK packet arriving first, the subsequent ICMP message can no +longer be mapped to the TCP socket as the sequence number has been updated when +the ACK is processed. On all modern OSes, nothing is done for the connection. +Although the original TCP connection is left in stalemate, the most OSes honor +the "invalid" ICMP message and cache the new PMTU so the subsequent TCP +connections to the host as long as the cached entry is valid(10 minutes). + +## Different result on various OSes +- Windows and FreeBSD(IOS and Macos): the ICMP message is honored "globally" - + subsequent TCP connections will use the cached PMTU, giving positive result +- Linux: the ICMP messages not mapped to any active socket are ignored + +In the function `tcp_v6_err()` from Linux kernel `net/ipv6/tcp_ipv6.c`: +https://github.com/torvalds/linux/blob/4376e966ecb78c520b0faf239d118ecfab42a119/net/ipv6/tcp_ipv6.c#L436C1-L436C35 + +```c + if (sk->sk_state != TCP_LISTEN && + !between(seq, snd_una, tp->snd_nxt)) { + __NET_INC_STATS(net, LINUX_MIB_OUTOFWINDOWICMPS); + goto out; + } +``` + +`snd_una` and `tp->snd_nxt` should be the same value because there is no packet +sent to the server after the initial large packet. `seq` is extracted from the +TCP header in the ICMP message payload. It does not fall into the range because +the values are updated by the ACK packet. + +The `LINUX_MIB_OUTOFWINDOWICMPS` counter can be checked using the command: +```sh +netstat -ts | grep -i icmp +``` + +Output: +``` +IcmpMsg: + 5 ICMP packets dropped because they were out-of-window +``` + +## WAN optimization of Tele2 +At first, oblivious of the fact that the large packet of culprit is ACK'd by the +test host, I focused on the fact that the window size of the TCP packet returned +in the ICMPv6 message is somehow altered by the ISP nodes. I confirmed this by +doing the test on an AWS instance. It seems that the AWS does not alter the +contents of TCP packets in any way. After a brief searching, I found that some +WAN optimization and QoS implementations alter the window size value of TCP +packets. Again, this had nothing to do with the problem: Linux kernel does not +care about the window value when mapping the raw packets to the sockets. + +The out of order issue is probably from mult-path set up between the ISP +nodes(rr L2 bonding, routers with same cost ...) and/or active queue management. +An ACK packet with no payload is smaller than an ICMPv6 message with payload so +it will have higher chance of being processed first. Not ideal(forcing endpoints +to utilize more memory for reordering), but modern systems are implemented to +work under these conditions. |
